What is Creatine? Health Benefits, Health Risks and More
Creatine is a natural compound in the human body and is primarily known for its use in sports.
Creatine has been studied extensively in the past few decades and has been found to provide some benefits and speed up muscle growth. Also, creatine has been found to help with fat loss and brain function.
What's is creatine:
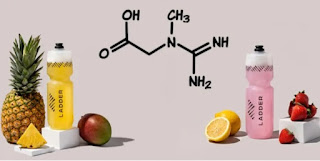
Creatine is an amino acid found mainly in the muscles and brain of your body. Although at far lower amounts than those seen in supplements derived from synthetic creatine, most individuals obtain creatine from seafood and red meat. Each day, the body's liver, pancreas, and kidneys may produce roughly 1 gram of creatine.
Your muscles are where your body stores creatine as phosphocreatine, where it is largely used as an energy source. People, therefore, use creatine orally to enhance sports performance and build muscle.
Additionally, several brain diseases, neuromuscular issues, congestive heart failure, and other illnesses are treated with oral creatine. Skin aging may be treated using topical creatine.
According to studies on the utilization of creatine for various ailments and activities:
Muscular size, performance, and strength. Oral creatine may enable an athlete to exert more effort during sprints or repetitions, resulting in a higher power, muscle mass, and performance improvements. Athletes who engage in high-intensity intermittent activities that call for a quick recovery during practice and competition frequently utilize creatine.
1- Injury avoidance. The frequency of dehydration, cramping in the muscles, and damage to the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves may be decreased by oral creatine.
2- Uncommon syndromes that metabolize creatine. Oral creatine supplementation may help some symptoms in kids with specific creatine-deficient diseases.
3- Cognition and mental well-being. Supplementing with creatine may enhance cognitive performance, particularly in elderly persons.
4- Bone health and sarcopenia. Supplementing with creatine may help slow down the loss of bone mineral density and skeletal muscle with aging.
5- A heart attack. For the treatment of heart failure, oral creatine is not supported by substantial research.
6- Skin ageing According to preliminary studies, men's skin sagging and wrinkles may be lessened by using a cream containing creatine and other chemicals on their faces every day for six weeks. According to a different study, a lotion with creatine and folic acid improves UV damage and minimizes wrinkles.
The most significant advantage of creatine supplementation appears to be for those with low amounts of creatine, such as vegetarians.
Our view :
Sprinters, weight lifters, and athletes who compete in team sports may find creatine useful if they need quick bursts of speed or improved physical strength.
While not all athletes will benefit from using creatine, data shows that it typically won't harm if taken as prescribed.
Although an older case study revealed that creatine could make renal diseases worse in patients, creatine doesn't seem to have an impact on kidney function in healthy individuals.
Security and adverse effects :
Creatine is probably safe to consume for up to five years when taken orally in the right dosage. As with any dietary supplement, it's crucial to pick a product that adheres to industry standards for manufacture and accepts third-party testing to guarantee product quality.
Creatine may result in:
1- Generally speaking, weight growth as lean body mass
2- Creatine might not be safe for those with the renal disease already present. However, more study is required.
Interactions
There might be interactions with:
Caffeine. The effectiveness of creatine may be reduced when used with coffee. Parkinson's disease may worsen if creatine is taken with more than 300 mg of caffeine daily. More investigation is required.